Appliation note
Control of Polymerization
Vaisala
In-line process and product quality control in polymerization process
Polymerization is the process of combining monomers into large polymer molecules. If the polymer contains two or more types of monomers , the process is knows as copolymerization.
On an industrial scale, the polymerization is conducted using five basic methods: bulk, solution, suspension, emulsion, and gas-phase.
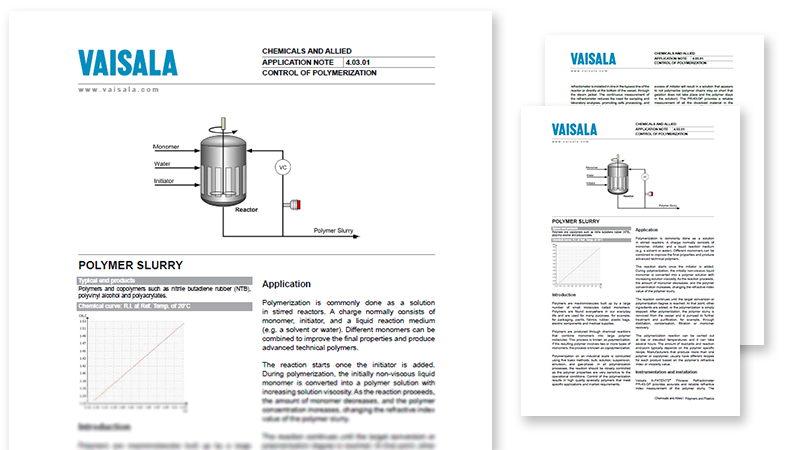
Polymerization is commonly done as a solution in stirred reactors. A charge normally consists of monomer, initiator, and a liquid reaction medium
(e.g. a solvent or water). Different monomers can be combined to improve the final properties and produce advanced technical polymers.
Vaisala Polaris™ Process Refractometer provides accurate and reliable refractive index measurement of the polymer slurry.
Installed directly in the bypass line of the reactor or at the bottom of the vessel, the in-line refractometer measurement reduces the need for sampling and laboratory analyses, ensuring safe processing, and increased productivity.
Changes in the refractive index can be monitored in real-time to follow closely the polymerization reaction and the degree of polymerization,
indicating when the target conversion and reaction end-point are achieved.
Conventional methods to monitor polymerization, such as Gas Chromatography (GC) or laboratory tests, require time-consuming sampling and analyses.
In-line viscosity is also widely use for monitoring polymerization. However, some polymerization reactions are very sensitive to the amount or concentration of charged initiator.
Learn about the numerous benefits of the refractometer measurement in polymerization process from the application note.
Download the application note in PDF by filling the form.
Go back to all Chemicals & Allied Products applications
You can modify your preference settings or unsubscribe at any time here